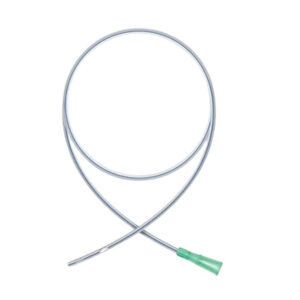
Infant Feeding Tube
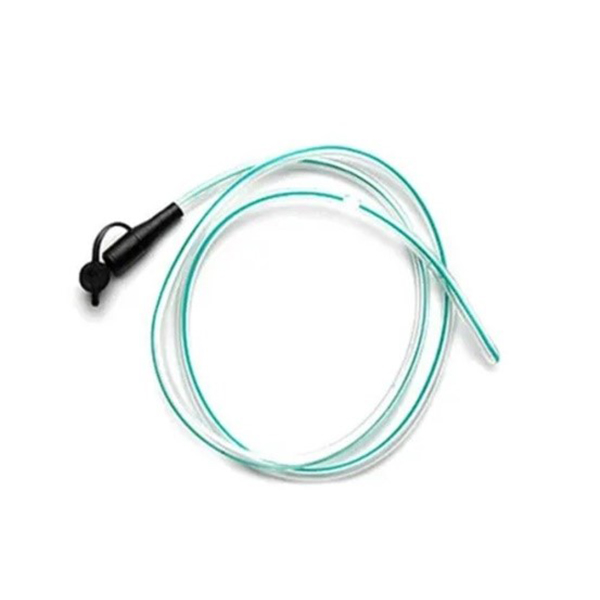
Infant feeding tubes, also known as gavage tubes or enteral feeding tubes, are small, soft, flexible tubes used to deliver nutrition and medication to infants who are unable to feed adequately or safely by mouth.
Minimum Quantity Order: 2000 Unit
Price: Negotiable
Product Enquiry Form
Sharing is caring:-
Description
Infant feeding tubes, also known as gavage tubes or enteral feeding tubes, are small, soft, flexible tubes used to deliver nutrition and medication to infants who are unable to feed adequately or safely by mouth.
Key features and characteristics
- Size and Material: Infant feeding tubes are typically sized between 5 and 9 French units and made from soft, non-toxic, medical-grade polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane.
- Design: The distal end (the part inserted into the infant) is cone-shaped and features two lateral eyes. Some tubes may include a guidewire to aid in insertion, which is removed after placement. The proximal end features a female luer mount for easy connection to a feeding syringe.
- Radio-opaque Line: Many infant feeding tubes have a radio-opaque line that allows for easy visibility and confirmation of placement via X-ray imaging.
- Graduated Scale: Most infant feeding tubes are marked at regular intervals (e.g., every centimeter) from the tip, typically starting at 5 cm and extending up to 40 cm, to assist in accurate insertion and placement.
- Sterility: Infant feeding tubes are disposable and typically provided in a pre-sterile pack, sterilized by irradiation.
Purpose and usage:
- Nutritional support: Feeding tubes are used to provide essential nutrients, including formula or breast milk, to infants who cannot obtain sufficient nourishment through breastfeeding or bottle-feeding due to various reasons, such as prematurity, medical conditions affecting feeding, or difficulty with sucking and swallowing.
- Medication administration: Feeding tubes can also be used to administer medications to infants who are unable to swallow pills or require medications that need to be taken with food.
- Short-term and long-term use: Nasogastric (NG) tubes, inserted through the nose into the stomach, are typically used for temporary feeding, usually for a few weeks or months.
Placement and care:
- Insertion: Feeding tubes are gently inserted through the nostril (nasogastric or NG tube) or mouth (orogastric or OG tube) and guided down the esophagus into the stomach.
- Confirmation of Placement: After insertion, the placement of the tube is confirmed to ensure it’s in the stomach and not the lungs. This can be done by aspirating a small amount of stomach fluid and testing its pH (stomach fluid will be acidic) or by X-ray.
- Securing the Tube: Once confirmed, the feeding tube is secured to the infant’s cheek with tape or other appropriate adhesives.
- Maintenance: The tube site needs regular cleaning and the tube should be flushed with water after feedings and medication administration to prevent clogging.
In summary, infant feeding tubes are valuable medical devices that help ensure infants receive the necessary nutrition and medication, promoting their growth and development, especially in situations where oral feeding is not feasible or safe.