Syringe
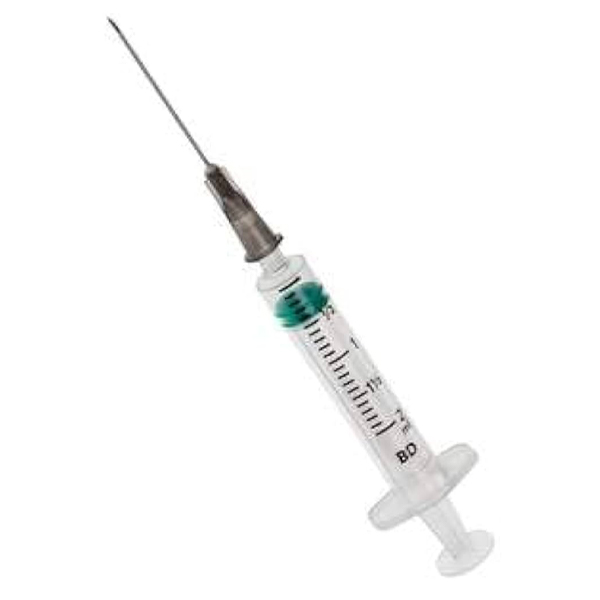
A syringe is a crucial medical device used for injecting or withdrawing fluids or gases from the body.
Minimum Quantity Order: 2000 Unit
Price: Negotiable
Product Enquiry Form
Category Surgical
Sharing is caring:-
Description
A syringe is a crucial medical device used for injecting or withdrawing fluids or gases from the body.
Key features of our Syringes:
- Barrel: A clear, cylindrical tube that holds the fluid and has graduated markings to measure the volume.
- Plunger: A movable rod or piston that fits snugly within the barrel and is used to draw in or push out the fluid.
- Needle (optional): A hollow, sharp tube that attaches to the syringe tip, allowing penetration of the skin or other tissues for injection or withdrawal.
- Tip designs: Syringes can have different tip designs, such as Luer lock, which twists to securely fasten the needle, or slip tip, which allows the needle to be pushed on and held by friction.
How it works
- Filling: The plunger is pulled back, creating a vacuum inside the barrel, drawing fluid in through the attached needle or nozzle.
- Injecting/Withdrawing: The plunger is pushed to expel the fluid, or pulled to withdraw fluid, with the needle or nozzle directing the flow.
Uses
Syringes are widely used in healthcare for various purposes, including:
- Medication administration: Delivering injections (intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal, intravenous) and vaccinations.
- Blood draws: Collecting blood samples for diagnosis and monitoring.
- Fluid aspiration and irrigation: Removing fluids from body cavities (e.g., abscesses) or cleaning wounds.
- Other applications: Used in laboratory research, dentistry (dental syringes), for oral medication administration (oral syringes), and in some veterinary and industrial applications.
Types
Syringes come in various sizes (e.g., 1ml, 2ml, 3ml, 5ml, 10ml, 20ml) and designs, including:
- Disposable syringes: Made of plastic and designed for single use, reducing the risk of contamination.
- Safety syringes: Equipped with safety features like retractable needles or safety shields to prevent needlestick injuries.
- Insulin syringes: Small syringes with fine needles and markings in insulin units, ensure precise dosing for diabetic patients.